 NW066 1/144 Atlas D - Project FIRE
NW066 1/144 Atlas D - Project FIRE NW066 1/144 Atlas D - Project FIRE
NW066 1/144 Atlas D - Project FIRE
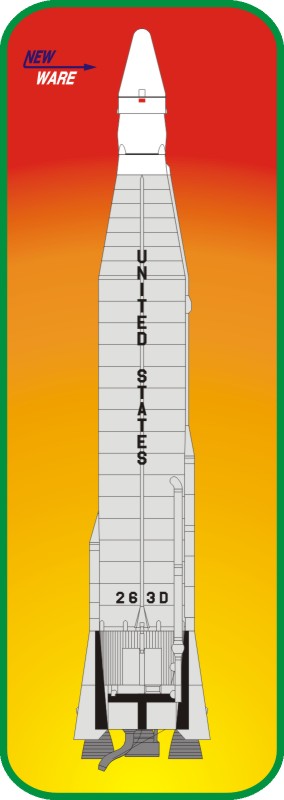
In 1955 Convair won the prime contract for Atlas ICBM.The
liquid oxygen and kerosene vehicle was designed to carry a
thermonuclear warhead over 7000 miles. The Atlas was unique in
its “stage and half” design in which two of its main engines
were shed to reduce weight after two minutes of flight, while the
central sustainer continued to burn. In order to minimize
sustainer tank weight (used also for booster engines), Convair
employeed balloon construction. Flights of Atlas began on June
11, 1957, with the launch of Atlas A powered by booster alone. In
November 1958, an Atlas B reached full design range, and the
operational Atlas D was deployed in 1960.
Project FIRE was to simulate reentry from a lunar mission. An
Atlas D booster lifted an instrumented payload (looking like a
miniature Apollo CM) to an altitude of 120 km. The velocity
package then fired the reentry vehicle into a -15 degree
trajectory at a velocity of 11 300 meters per second.
First of two launches occured at ¨April 14th, 1964. The
spacecraft exterior reached an estimated temperature of 11 400 K
(20 000 degrees F). The mission provided reentry heating
measurements needed to evaluate heatshield materials and
information on the communication blackout during reentry.